42. Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
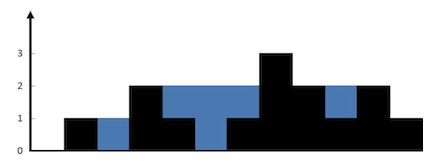
The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example
Input: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
题意:这道题是给了一个数组,里面的值代表柱子的高低。问如果下雨,问以柱子的形状来看,最多可以存多少水。 这个题有多种解法。 下面列出两种。
解法1:我们对每一个柱子来看,就这个柱子而言, 我们看它的顶上最多可以放多少水。这样对每一个柱子进行计算相加即可。 而决定每一个柱子之上能放多少水,是它左右两边最高的柱子中矮的那根决定的。 因为我们可以开两个数组, 一个 $left$ 和一个 $right$ 分别存放 $i$ 左边和右边的最大值。 这样使得复杂度在 $O(n)$ 时间解决。
代码
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if(height == null) return 0;
int[] left = new int[height.length];
int[] right = new int[height.length];
left[0] = height[0];
for(int i = 1; i < height.length; i++) {
left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1], height[i]);
}
right[height.length - 1] = height[height.length - 1];
for (int i = height.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
right[i] = Math.max(right[i + 1], height[i]);
}
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < height.length - 1; i++) {
ret += Math.min(left[i], right[i]) - height[i];
}
return ret;
}
}
解法2:既然解法 1 是竖着计算每条柱子。那么这个方法就是横着计算水量。 所以对于任何一条柱子来说,我们需要找出比它高的最近左右两根柱子,当前的柱子可以看作是池底。 如果我使用单调递减栈来做的话, 左边的柱子的信息一直都维护在栈里,所以,每次发现有新的柱子比栈顶要高的话,我们便可以 pop 出站进行计算。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int i = 0, ret = 0;
while(i < height.length) {
if(!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) {
int bottom = stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()) continue;
ret += (Math.min(height[stack.peek()], height[i]) - height[bottom]) * (i - stack.peek() - 1);
} else {
stack.push(i);
i++;
}
}
return ret;
}
}