218. The Skyline Problem
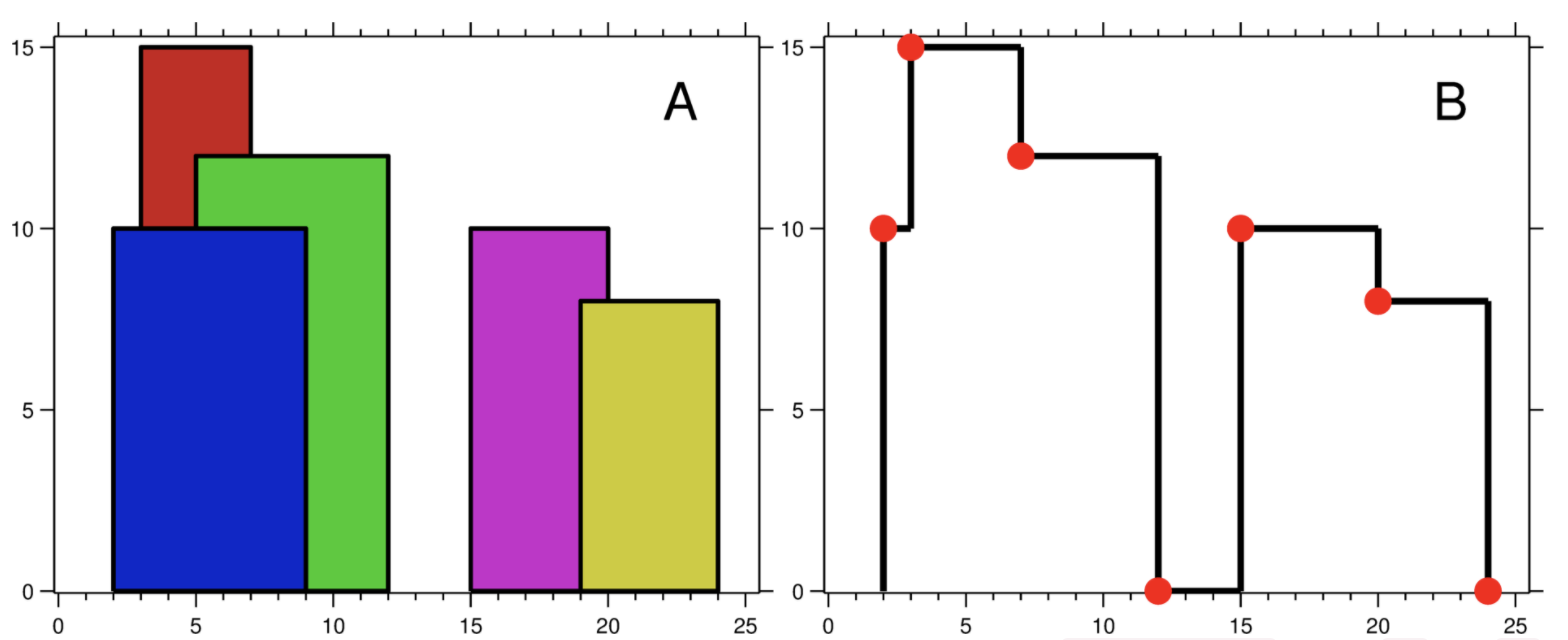
A city’s skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Now suppose you are given the locations and height of all the buildings as shown on a cityscape photo (Figure A), write a program to output the skyline formed by these buildings collectively (Figure B).
The geometric information of each building is represented by a triplet of integers [Li, Ri, Hi], where Li and Ri are the x coordinates of the left and right edge of the ith building, respectively, and Hi is its height. It is guaranteed that 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX, and Ri - Li > 0. You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
For instance, the dimensions of all buildings in Figure A are recorded as: [ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ] .
The output is a list of “key points” (red dots in Figure B) in the format of [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], … ] that uniquely defines a skyline. A key point is the left endpoint of a horizontal line segment. Note that the last key point, where the rightmost building ends, is merely used to mark the termination of the skyline, and always has zero height. Also, the ground in between any two adjacent buildings should be considered part of the skyline contour.
For instance, the skyline in Figure B should be represented as:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ].
Notes:
The number of buildings in any input list is guaranteed to be in the range [0, 10000]. The input list is already sorted in ascending order by the left x position Li. The output list must be sorted by the x position. There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance, […[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]…] is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such: […[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], …]
题意:这个题是说有一些城市的建筑,用一个数组代表每一个建筑的宽度和高度, 问最后在正视图里面,我们看到的轮廓是什么样的。
观察已给的例子, 我们可以发现只需要找出那些变化点的坐标就可以了。 这道题和最少 meeting room 很像,我们需要用一个线扫一遍,在每一个 point 上我们都找出最大的值,如果当前的高度和之前的高度不一样,那么我们就需要把这个值加入最终结果。
剩下的就是实现技巧。 从以上分析,发现需要找到一个数据结构,能够快速删除一个数, 能够快速返回当前最大值, 快速插入数值。 因此 treemap 就非常合适。 因为 treemap 这些操作都是 logn 时间解决的。 这里需要注意,1. 对于每一个 building, 我们都需要拆分数组,遇到起点需要插入 treemap, 遇到终点需要对应删除。 我们可以用负数来代表楼的右边界。 而且我们需要对这些已经拆分好的数组重新按照 x 坐标排序, 对于 x 相同的情况,高的楼排前面,因为低的那个点不会对轮廓造成影响。 2. 对于相同高度的房子,我们可以把他考虑成一个,因次 treemap 里面的 key 应该是楼的高度, value 是相同高度楼的个数。每当个数为 0 的时候,我们需要对应删除。 3. 需要考虑 treemap 为空的情况。 或者从一开始就 push 一个基数进去。
代码
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < buildings.length; i++) {
int[] start = new int[]{buildings[i][0], buildings[i][2]};
int[] end = new int[]{buildings[i][1], -buildings[i][2]};
list.add(start);
list.add(end);
}
Collections.sort(list, (a, b) -> {
if(a[0] != b[0])
return a[0] - b[0];
return b[1] - a[1];
});
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> tm = new TreeMap<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int prev = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) {
int x = list.get(i)[0], y = list.get(i)[1];
if(y > 0) {
if(tm.containsKey(y)) tm.put(y, tm.get(y) + 1);
else tm.put(y, 1);
} else {
if(tm.containsKey(-y)) {
if(tm.get(-y) == 1) tm.remove(-y);
else tm.put(-y, tm.get(-y) - 1);
}
}
if(tm.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> tmp = Arrays.asList(x,0);
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
prev = 0;
} else {
if( prev != tm.firstKey()) {
List<Integer> tmp = Arrays.asList(x,tm.firstKey());
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
prev = tm.firstKey();
}
}
}
return ret;
}
}